Abstract
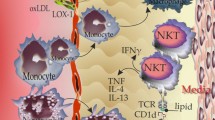
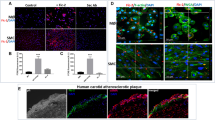
This review focuses on new aspects of extracellular roles of the calgranulins. S100A8, S100A9 and S100A12 are constitutively expressed in neutrophils and induced in several cell types. The S100A8 and S100A9 genes are regulated by pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators and their functions may depend on cell type, mediators within a particular inflammatory milieu, receptors involved in their recognition and their post-translational modification. The S100A8 gene induction in macrophages is dependent on IL-10 and potentiated by immunosuppressive agents. S100A8 and S100A9 are oxidized by peroxide, hypochlorite and nitric oxide (NO). HOCl generates intra-chain sulfinamide bonds; stronger oxidation promotes cross-linked forms that are seen in human atheroma. S100A8 is >200-fold more sensitive to oxidative cross-linking than low-density lipoprotein and may reduce oxidative damage. S100A8 and S100A9 can be S-nitrosylated. S100A8–SNO suppresses mast cell activation and inflammation in the microcirculation and may act as an NO transporter to regulate vessel tone in inflammatory lesions. S100A12 activates mast cells and is a monocyte and mast cell chemoattractant; a G-protein-coupled mechanism may be involved. Structure–function studies are discussed in relation to conservation and divergence of functions in S100A8. S100A12 induces cytokines in mast cells, but not monocytes/macrophages. It forms complexes with Zn2+ and, by chelating Zn2+, S100A12 significantly inhibits MMPs. Zn2+ in S100A12 complexes co-localize with MMP-9 in foam cells in atheroma. In summary, S100A12 has pro-inflammatory properties that are likely to be stable in an oxidative environment, because it lacks Cys and Met residues. Conversely, S100A8 and S100A9 oxidation and S-nitrosylation may have important protective mechanisms in inflammation.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- mS100A8:
-
Murine S100A8
- mS100A9:
-
Murine S100A9
- TNFα:
-
Tumor necrosis factor α
- TGFβ:
-
Transforming growth factor β
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- COX-2:
-
Cyclo-oxygenase 2
- cAMP:
-
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- MAP kinase:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- EC:
-
Endothelial cells
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factor
- GC:
-
Glucocorticoids
- DEX:
-
Dexamethasone
- PPAR-γ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ
- RAGE:
-
Receptor for advanced glycation end products
- NFκB:
-
Nuclear factor κB
- EN-RAGE:
-
Extracellular newly identified RAGE-binding protein
- AGE:
-
Advanced glycation end products
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemotactic protein 1
- NIF:
-
Neutrophil immobilizing factor
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- MPO:
-
Myeloperoxidase
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
References
Adami C, Bianchi R, Pula G, Donato R (2004) S100B-stimulated NO production by BV-2 microglia is independent of RAGE transducing activity but dependent on RAGE extracellular domain. Biochim Biophys Acta 1742:169–177
Aguiar-Passeti T, Postol E, Sorg C, Mariano M (1997) Epithelioid cells from foreign-body granuloma selectively express the calcium-binding protein MRP-14, a novel down-regulatory molecule of macrophage activation. J Leukoc Biol 62:852–858
Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Katoh M, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1994) Expression of MRP14, 27E10, interferon-alpha and leukocyte common antigen by reactive microglia in postmortem human brain tissue. J Neuroimmunol 50:195–201
Akpek EK, Liu SH, Thompson R, Gottsch JD (2002) Identification of paramyosin as a binding protein for calgranulin C in experimental helminthic keratitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:2677–2684
Anceriz N, Vandal K, Tessier PA (2007) S100A9 mediates neutrophil adhesion to fibronectin through activation of beta2 integrins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354:84–89
Bai B, Yamamoto K, Sato H, Sugiura H, Tanaka T (2007) Complex regulation of S100A8 by IL-17, dexamethasone, IL-4 and IL-13 in HaCat cells (human keratinocyte cell line). J Dermatol Sci 47:259–262
Baldassarre ME, Altomare MA, Fanelli M, Carbone D, Di Bitonto G, Mautone A, Laforgia N (2007) Does calprotectin represent a regulatory factor in host defense or a drug target in inflammatory disease? Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 7:1–5
Basso D, Greco E, Fogar P, Pucci P, Flagiello A, Baldo G, Giunco S, Valerio A, Navaglia F, Zambon CF, Falda A, Pedrazzoli S, Plebani M (2006) Pancreatic cancer-derived S-100A8 N-terminal peptide: a diabetes cause? Clin Chim Acta 372:120–128
Bausinger H, Lipsker D, Ziylan U, Manie S, Briand JP, Cazenave JP, Muller S, Haeuw JF, Ravanat C, de la Salle H, Hanau D (2002) Endotoxin-free heat-shock protein 70 fails to induce APC activation. Eur J Immunol 32:3708–3713
Berntzen HB, Fagerhol MK (1988) L1, a major granulocyte protein: antigenic properties of its subunits. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 48:647–652
Bianchi R, Adami C, Giambanco I, Donato R (2007) S100B binding to RAGE in microglia stimulates COX-2 expression. J Leukoc Biol 81:108–118
Bianchi R, Giambanco I, Donato R (2008) S100B/RAGE-dependent activation of microglia via NF-kappaB and AP-1 Co-regulation of COX-2 expression by S100B, IL-1beta and TNF-alpha. Neurobiol Aging
Bierhaus A, Humpert PM, Morcos M, Wendt T, Chavakis T, Arnold B, Stern DM, Nawroth PP (2005) Understanding RAGE, the receptor for advanced glycation end products. J Mol Med 83:876–886
Bischoff SC (2007) Role of mast cells in allergic and non-allergic immune responses: comparison of human and murine data. Nat Rev Immunol 7:93–104
Boyd JH, Kan B, Roberts H, Wang Y, Walley KR (2008) S100A8 and S100A9 mediate endotoxin-induced cardiomyocyte dysfunction via the receptor for advanced glycation end products. Circ Res 102:1239–1246
Bozinovski S, Cross M, Vlahos R, Jones JE, Hsuu K, Tessier PA, Reynolds EC, Hume DA, Hamilton JA, Geczy CL, Anderson GP (2005) S100A8 chemotactic protein is abundantly increased, but only a minor contributor to LPS-induced, steroid resistant neutrophilic lung inflammation in vivo. J Proteome Res 4:136–145
Brun JG, Haland G, Haga HJ, Fagerhol MK, Jonsson R (1995) Effects of calprotectin in avridine-induced arthritis. Apmis 103:233–240
Champaiboon C, Sappington KJ, Guenther BD, Ross KF, Herzberg MC (2009) Calprotectin S100A9 calcium-binding loops I and II are essential for keratinocyte resistance to bacterial invasion. J Biol Chem 284:7078–7090
Cole AM, Kim YH, Tahk S, Hong T, Weis P, Waring AJ, Ganz T (2001) Calcitermin, a novel antimicrobial peptide isolated from human airway secretions. FEBS Lett 504:5–10
Coleman N, Stanley MA (1994) Expression of the myelomonocytic antigens CD36 and L1 by keratinocytes in squamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervix. Hum Pathol 25:73–79
Cornish CJ, Devery JM, Poronnik P, Lackmann M, Cook DI, Geczy CL (1996) S100 protein CP-10 stimulates myeloid cell chemotaxis without activation. J Cell Physiol 166:427–437
Couper KN, Blount DG, Riley EM (2008) IL-10: the master regulator of immunity to infection. J Immunol 180:5771–5777
Dale CS, Goncalves LR, Juliano L, Juliano MA, da Silva AM, Giorgi R (2004) The C-terminus of murine S100A9 inhibits hyperalgesia and edema induced by jararhagin. Peptides 25:81–89
Dale CS, Pagano Rde L, Paccola CC, Pinotti-Guirao T, Juliano MA, Juliano L, Giorgi R (2006) Effect of the C-terminus of murine S100A9 protein on experimental nociception. Peptides 27:2794–2802
Delabie J, de Wolf-Peeters C, van den Oord JJ, Desmet VJ (1990) Differential expression of the calcium-binding proteins MRP8 and MRP14 in granulomatous conditions: an immunohistochemical study. Clin Exp Immunol 81:123–126
Devery JM, King NJ, Geczy CL (1994) Acute inflammatory activity of the S100 protein CP-10. Activation of neutrophils in vivo and in vitro. J Immunol 152:1888–1897
Donato R (2003) Intracellular and extracellular roles of S100 proteins. Microsc Res Tech 60:540–551
Eckert RL, Broome AM, Ruse M, Robinson N, Ryan D, Lee K (2004) S100 proteins in the epidermis. J Invest Dermatol 123:23–33
Edgeworth J, Gorman M, Bennett R, Freemont P, Hogg N (1991) Identification of p8, 14 as a highly abundant heterodimeric calcium binding protein complex of myeloid cells. J Biol Chem 266:7706–7713
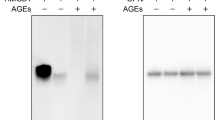
Ehlermann P, Eggers K, Bierhaus A, Most P, Weichenhan D, Greten J, Nawroth PP, Katus HA, Remppis A (2006) Increased proinflammatory endothelial response to S100A8/A9 after preactivation through advanced glycation end products. Cardiovasc Diabetol 5:6
Endoh Y, Chung YM, Clark IA, Geczy CL, Hsu K (2009) IL-10-dependent S100A8 gene induction in monocytes/macrophages by double-stranded RNA. J Immunol 182:2258–2268
Eue I, Langer C, Eckardstein A, Sorg C (2000a) Myeloid related protein (MRP) 14 expressing monocytes infiltrate atherosclerotic lesions of ApoE null mice. Atherosclerosis 151:593–597
Eue I, Pietz B, Storck J, Klempt M, Sorg C (2000b) Transendothelial migration of 27E10 + human monocytes. Int Immunol 12:1593–1604
Eversole LR, Miyasaki KT, Christensen RE (1992) The distribution of the antimicrobial protein, calprotectin, in normal oral keratinocytes. Arch Oral Biol 37:963–968
Eversole LR, Miyasaki KT, Christensen RE (1993) Keratinocyte expression of calprotectin in oral inflammatory mucosal diseases. J Oral Pathol Med 22:303–307
Foell D, Kucharzik T, Kraft M, Vogl T, Sorg C, Domschke W, Roth J (2003) Neutrophil derived human S100A12 (EN-RAGE) is strongly expressed during chronic active inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 52:847–853
Foell D, Frosch M, Sorg C, Roth J (2004a) Phagocyte-specific calcium-binding S100 proteins as clinical laboratory markers of inflammation. Clin Chim Acta 344:37–51
Foell D, Hernandez-Rodriguez J, Sanchez M, Vogl T, Cid MC, Roth J (2004b) Early recruitment of phagocytes contributes to the vascular inflammation of giant cell arteritis. J Pathol 204:311–316
Foell D, Wittkowski H, Vogl T, Roth J (2007) S100 proteins expressed in phagocytes: a novel group of damage-associated molecular pattern molecules. J Leukoc Biol 81:28–37
Foell D, Wittkowski H, Roth J (2009) Monitoring disease activity by stool analyses: from occult blood to molecular markers of intestinal inflammation and damage. Gut 58:859–868
Freemont P, Hogg N, Edgeworth J (1989) Sequence identity. Nature 339:516
Frosch M, Strey A, Vogl T, Wulffraat NM, Kuis W, Sunderkotter C, Harms E, Sorg C, Roth J (2000) Myeloid-related proteins 8 and 14 are specifically secreted during interaction of phagocytes and activated endothelium and are useful markers for monitoring disease activity in pauciarticular-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:628–637
Fu X, Mueller DM, Heinecke JW (2002) Generation of intramolecular and intermolecular sulfenamides, sulfinamides, and sulfonamides by hypochlorous acid: a potential pathway for oxidative cross-linking of low-density lipoprotein by myeloperoxidase. Biochemistry 41:1293–1301
Gabrielsen TO, Dale I, Brandtzaeg P, Hoel PS, Fagerhol MK, Larsen TE, Thune PO (1986) Epidermal and dermal distribution of a myelomonocytic antigen (L1) shared by epithelial cells in various inflammatory skin diseases. J Am Acad Dermatol 15:173–179
Galli SJ, Nakae S, Tsai M (2005) Mast cells in the development of adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol 6:135–142
Gao B, Tsan MF (2003a) Endotoxin contamination in recombinant human heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) preparation is responsible for the induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha release by murine macrophages. J Biol Chem 278:174–179
Gao B, Tsan MF (2003b) Recombinant human heat shock protein 60 does not induce the release of tumor necrosis factor alpha from murine macrophages. J Biol Chem 278:22523–22529
Gebhardt C, Breitenbach U, Tuckermann JP, Dittrich BT, Richter KH, Angel P (2002) Calgranulins S100A8 and S100A9 are negatively regulated by glucocorticoids in a c-Fos-dependent manner and overexpressed throughout skin carcinogenesis. Oncogene 21:4266–4276
Gebhardt C, Nemeth J, Angel P, Hess J (2006) S100A8 and S100A9 in inflammation and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 72:1622–1631
Geczy C (1996) Regulation and proinflammatory properties of the chemotactic protein, CP-10. Biochim Biophys Acta 1313:246–252
Ghavami S, Kerkhoff C, Los M, Hashemi M, Sorg C, Karami-Tehrani F (2004) Mechanism of apoptosis induced by S100A8/A9 in colon cancer cell lines: the role of ROS and the effect of metal ions. J Leukoc Biol 76:169–175
Ghavami S, Kerkhoff C, Chazin WJ, Kadkhoda K, Xiao W, Zuse A, Hashemi M, Eshraghi M, Schulze-Osthoff K, Klonisch T, Los M (2008a) S100A8/9 induces cell death via a novel, RAGE-independent pathway that involves selective release of Smac/DIABLO and Omi/HtrA2. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783:297–311
Ghavami S, Rashedi I, Dattilo BM, Eshraghi M, Chazin WJ, Hashemi M, Wesselborg S, Kerkhoff C, Los M (2008b) S100A8/A9 at low concentration promotes tumor cell growth via RAGE ligation and MAP kinase-dependent pathway. J Leukoc Biol 83:1484–1492
Glaser R, Harder J, Lange H, Bartels J, Christophers E, Schroder JM (2005) Antimicrobial psoriasin (S100A7) protects human skin from Escherichia coli infection. Nat Immunol 6:57–64
Goebeler M, Roth J, Burwinkel F, Vollmer E, Bocker W, Sorg C (1994) Expression and complex formation of S100-like proteins MRP8 and MRP14 by macrophages during renal allograft rejection. Transplantation 58:355–361
Goetzl EJ, Austen KF (1972) A neutrophil-immobilizing factor derived from human leukocytes, I: generation and partial characterization. J Exp Med 136:1564–1580
Goetzl EJ, Gigli I, Wasserman S, Austen KF (1973) A neutrophil immobilizing factor derived from human leukocytes, II: specificity of action on polymorphonuclear leukocyte mobility. J Immunol 111:938–945
Gordon S (2003) Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol 3:23–35
Gottsch JD, Liu SH, Minkovitz JB, Goodman DF, Srinivasan M, Stark WJ (1995) Autoimmunity to a cornea-associated stromal antigen in patients with Mooren’s ulcer. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 36:1541–1547
Gottsch JD, Eisinger SW, Liu SH, Scott AL (1999a) Calgranulin C has filariacidal and filariastatic activity. Infect Immun 67:6631–6636
Gottsch JD, Li Q, Ashraf F, O’Brien TP, Stark WJ, Liu SH (1999b) Cytokine-induced calgranulin C expression in keratocytes. Clin Immunol 91:34–40
Goyette J, Yan WX, Yamen E, Chung YM, Lim SY, Hsu K, Rahimi F, di Girolamo N, Song C, Jessup W, Kockx M, Bobryshev YV, Freedman SB, Geczy C (2009) Pleiotropic roles of S100A12 in coronary atherosclerotic plaque formation and rupture. J Immunol 183(1):593–603
Greenlee KJ, Corry DB, Engler DA, Matsunami RK, Tessier P, Cook RG, Werb Z, Kheradmand F (2006) Proteomic identification of in vivo substrates for matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 reveals a mechanism for resolution of inflammation. J Immunol 177:7312–7321
Gribenko AV, Makhatadze GI (1998) Oligomerization and divalent ion binding properties of the S100P protein: a Ca2 +/Mg2 + -switch model. J Mol Biol 283:679–694
Grimbaldeston MA, Geczy CL, Tedla N, Finlay-Jones JJ, Hart PH (2003) S100A8 induction in keratinocytes by ultraviolet A irradiation is dependent on reactive oxygen intermediates. J Invest Dermatol 121:1168–1174
Guignard F, Mauel J, Markert M (1995) Identification and characterization of a novel human neutrophil protein related to the S100 family. Biochem J 309(Pt 2):395–401
Gurish MF, Austen KF (2001) The diverse roles of mast cells. J Exp Med 194:F1–F5
Harrison CA, Raftery MJ, Walsh J, Alewood P, Iismaa SE, Thliveris S, Geczy CL (1999) Oxidation regulates the inflammatory properties of the murine S100 protein S100A8. J Biol Chem 274:8561–8569
Hasegawa T, Kosaki A, Kimura T, Matsubara H, Mori Y, Okigaki M, Masaki H, Toyoda N, Inoue-Shibata M, Kimura Y, Nishikawa M, Iwasaka T (2003) The regulation of EN-RAGE (S100A12) gene expression in human THP-1 macrophages. Atherosclerosis 171:211–218
Hayashi N, Kido J, Kido R, Wada C, Kataoka M, Shinohara Y, Nagata T (2007) Regulation of calprotectin expression by interleukin-1alpha and transforming growth factor-beta in human gingival keratinocytes. J Periodontal Res 42:1–7
Hazell LJ, Stocker R (1993) Oxidation of low-density lipoprotein with hypochlorite causes transformation of the lipoprotein into a high-uptake form for macrophages. Biochem J 290:165–172
Hazell LJ, van den Berg JJ, Stocker R (1994) Oxidation of low-density lipoprotein by hypochlorite causes aggregation that is mediated by modification of lysine residues rather than lipid oxidation. Biochem J 302:297–304
Healy AM, Pickard MD, Pradhan AD, Wang Y, Chen Z, Croce K, Sakuma M, Shi C, Zago AC, Garasic J, Damokosh AI, Dowie TL, Poisson L, Lillie J, Libby P, Ridker PM, Simon DI (2006) Platelet expression profiling and clinical validation of myeloid-related protein-14 as a novel determinant of cardiovascular events. Circulation 113:2278–2284
Heizmann CW, Cox JA (1998) New perspectives on S100 proteins: a multi-functional Ca(2 +)-, Zn(2 +)- and Cu(2 +)-binding protein family. Biometals 11:383–397
Heizmann CW, Fritz G, Schafer BW (2002) S100 proteins: structure, functions and pathology. Front Biosci 7:d1356–d1368
Hermani A, De Servi B, Medunjanin S, Tessier PA, Mayer D (2006) S100A8 and S100A9 activate MAP kinase and NF-kappaB signaling pathways and trigger translocation of RAGE in human prostate cancer cells. Exp Cell Res 312:184–197
Hess DT, Matsumoto A, Kim S-O, Marshall HE, Stamler JS (2005) Protein S-nitrosylation: purview and parameters. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:150–166
Hessian PA, Edgeworth J, Hogg N (1993) MRP-8 and MRP-14, two abundant Ca(2 +)-binding proteins of neutrophils and monocytes. J Leukoc Biol 53:197–204
Hessian PA, Wilkinson L, Hogg N (1995) The S100 family protein MRP-14 (S100A9) has homology with the contact domain of high molecular weight kininogen. FEBS Lett 371:271–275
Hetland G, Talgo GJ, Fagerhol MK (1998) Chemotaxins C5a and fMLP induce release of calprotectin (leucocyte L1 protein) from polymorphonuclear cells in vitro. Mol Pathol 51:143–148
Hiratsuka S, Watanabe A, Aburatani H, Maru Y (2006) Tumour-mediated upregulation of chemoattractants and recruitment of myeloid cells predetermines lung metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 8:1369–1375
Hitomi J, Yamaguchi K, Kikuchi Y, Kimura T, Maruyama K, Nagasaki K (1996) A novel calcium-binding protein in amniotic fluid, CAAF1: its molecular cloning and tissue distribution. J Cell Sci 109(Pt 4):805–815
Hitomi J, Kimura T, Kusumi E, Nakagawa S, Kuwabara S, Hatakeyama K, Yamaguchi K (1998) Novel S100 proteins in human esophageal epithelial cells: CAAF1 expression is associated with cell growth arrest. Arch Histol Cytol 61:163–178
Hobbs JA, May R, Tanousis K, McNeill E, Mathies M, Gebhardt C, Henderson R, Robinson MJ, Hogg N (2003) Myeloid cell function in MRP-14 (S100A9) null mice. Mol Cell Biol 23:2564–2576
Hofmann MA, Drury S, Fu C, Qu W, Taguchi A, Lu Y, Avila C, Kambham N, Bierhaus A, Nawroth P, Neurath MF, Slattery T, Beach D, McClary J, Nagashima M, Morser J, Stern D, Schmidt AM (1999) RAGE mediates a novel proinflammatory axis: a central cell surface receptor for S100/calgranulin polypeptides. Cell 97:889–901
Hogg N, Allen C, Edgeworth J (1989) Monoclonal antibody 5.5 reacts with p8, 14, a myeloid molecule associated with some vascular endothelium. Eur J Immunol 19:1053–1061
Hsu K, Passey RJ, Endoh Y, Rahimi F, Youssef P, Yen T, Geczy CL (2005) Regulation of S100A8 by glucocorticoids. J Immunol 174:2318–2326
Hu SP, Harrison C, Xu K, Cornish CJ, Geczy CL (1996) Induction of the chemotactic S100 protein, CP-10, in monocyte/macrophages by lipopolysaccharide. Blood 87:3919–3928
Hunter MJ, Chazin WJ (1998) High level expression and dimer characterization of the S100 EF-hand proteins, migration inhibitory factor-related proteins 8 and 14. J Biol Chem 273:12427–12435
Ikemoto M, Murayama H, Itoh H, Totani M, Fujita M (2007) Intrinsic function of S100A8/A9 complex as an anti-inflammatory protein in liver injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. Clin Chim Acta 376:197–204
Isaksen B, Fagerhol MK (2001) Calprotectin inhibits matrix metalloproteinases by sequestration of zinc. Mol Pathol 54:289–292
Ishikawa K, Nakagawa A, Tanaka I, Suzuki M, Nishihira J (2000) The structure of human MRP8, a member of the S100 calcium-binding protein family, by MAD phasing at 1.9 A resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 56:559–566
Jaffrey SR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Ferris CD, Tempst P, Snyder SH (2001) Protein S-nitrosylation: a physiological signal for neuronal nitric oxide. Nat Cell Biol 3:193–197
Jinquan T, Vorum H, Larsen CG, Madsen P, Rasmussen HH, Gesser B, Etzerodt M, Honore B, Celis JE, Thestrup-Pedersen K (1996) Psoriasin: a novel chemotactic protein. J Invest Dermatol 107:5–10
Kerkhoff C, Sorg C, Tandon NN, Nacken W (2001) Interaction of S100A8/S100A9-arachidonic acid complexes with the scavenger receptor CD36 may facilitate fatty acid uptake by endothelial cells. Biochemistry 40:241–248
Kerkhoff C, Hofmann HA, Vormoor J, Melkonyan H, Roth J, Sorg C, Klempt M (2002) Binding of two nuclear complexes to a novel regulatory element within the human S100A9 promoter drives the S100A9 gene expression. J Biol Chem 277:41879–41887
Kerkhoff C, Nacken W, Benedyk M, Dagher MC, Sopalla C, Doussiere J (2005) The arachidonic acid-binding protein S100A8/A9 promotes NADPH oxidase activation by interaction with p67phox and Rac-2. Faseb J 19:467–469
Kido J, Hayashi N, Kataoka M, Nagata T (2005) Calprotectin expression in human monocytes: induction by porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin-1beta. J Periodontol 76:437–442
Klebanoff SJ (2005) Myeloperoxidase: friend and foe. J Leukoc Biol 77:598–625
Kligman D, Hilt DC (1988) The S100 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci 13:437–443
Koike T, Harada N, Yoshida T, Morikawa M (1992) Regulation of myeloid-specific calcium binding protein synthesis by cytosolic protein kinase C. J Biochem (Tokyo) 112:624–630
Komada T, Araki R, Nakatani K, Yada I, Naka M, Tanaka T (1996) Novel specific chemtactic receptor for S100L protein on guinea pig eosinophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 220:871–874
Korndorfer IP, Brueckner F, Skerra A (2007) The crystal structure of the human (S100A8/S100A9)2 heterotetramer, calprotectin, illustrates how conformational changes of interacting alpha-helices can determine specific association of two EF-hand proteins. J Mol Biol 370:887–898
Kube E, Becker T, Weber K, Gerke V (1992) Protein–protein interaction studied by site-directed mutagenesis: characterization of the annexin II-binding site on p11, a member of the S100 protein family. J Biol Chem 267:14175–14182
Kumar A, Steinkasserer A, Berchtold S (2003) Interleukin-10 influences the expression of MRP8 and MRP14 in human dendritic cells. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 132:40–47
Lackmann M, Cornish CJ, Simpson RJ, Moritz RL, Geczy CL (1992) Purification and structural analysis of a murine chemotactic cytokine (CP-10) with sequence homology to S100 proteins. J Biol Chem 267:7499–7504
Lackmann M, Rajasekariah P, Iismaa SE, Jones G, Cornish CJ, Hu S, Simpson RJ, Moritz RL, Geczy CL (1993) Identification of a chemotactic domain of the pro-inflammatory S100 protein CP-10. J Immunol 150:2981–2991
Lagasse E, Clerc RG (1988) Cloning and expression of two human genes encoding calcium-binding proteins that are regulated during myeloid differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 8:2402–2410
Lau D, Baldus S (2006) Myeloperoxidase and its contributory role in inflammatory vascular disease. Pharmacol Ther 111:16–26
Lau W, Devery JM, Geczy CL (1995) A chemotactic S100 peptide enhances scavenger receptor and Mac-1 expression and cholesteryl ester accumulation in murine peritoneal macrophages in vivo. J Clin Invest 95:1957–1965
Lazoura E, McLeish MJ, Aguilar MI (2000) Studies on the conformational properties of CP-10(42–55), the hinge region of CP-10, using circular dichroism and RP-HPLC. J Pept Res 55:411–418
Leach ST, Yang Z, Messina I, Song C, Geczy CL, Cunningham AM, Day AS (2007) Serum and mucosal S100 proteins, calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9) and S100A12, are elevated at diagnosis in children with inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 42:1321–1331
Leclerc E, Fritz G, Weibel M, Heizmann CW, Galichet A (2007) S100B and S100A6 differentially modulate cell survival by interacting with distinct RAGE (receptor for advanced glycation end products) immunoglobulin domains. J Biol Chem 282:31317–31331
Lee KC, Eckert RL (2007) S100A7 (Psoriasin)–mechanism of antibacterial action in wounds. J Invest Dermatol 127:945–957
Li J, Schmidt AM (1997) Characterization and functional analysis of the promoter of RAGE, the receptor for advanced glycation end products. J Biol Chem 272:16498–16506
Lim SY, Raftery M, Cai H, Hsu K, Yan WX, Hseih HL, Watts RN, Richardson D, Thomas S, Perry M, Geczy CL (2008) S-nitrosylated S100A8: novel anti-inflammatory properties. J Immunol 181:5627–5636
Lim SY, Raftery MJ, Goyette J, Hsu K and Geczy CL (2009). Oxidative modifications of S100 proteins: functional regulation by redox. J Leukoc Biol
Lusitani D, Malawista SE, Montgomery RR (2003) Calprotectin, an abundant cytosolic protein from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes, inhibits the growth of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun 71:4711–4716
Manitz MP, Horst B, Seeliger S, Strey A, Skryabin BV, Gunzer M, Frings W, Schonlau F, Roth J, Sorg C, Nacken W (2003) Loss of S100A9 (MRP14) results in reduced interleukin-8-induced CD11b surface expression, a polarized microfilament system, and diminished responsiveness to chemoattractants in vitro. Mol Cell Biol 23:1034–1043
McClintock KA, Shaw GS (2003) A novel S100 target conformation is revealed by the solution structure of the Ca2 + –S100B–TRTK-12 complex. J Biol Chem 278:6251–6257
McCormick MM, Rahimi F, Bobryshev YV, Gaus K, Zreiqat H, Cai H, Lord RS, Geczy CL (2005) S100A8 and S100A9 in human arterial wall. Implications for atherogenesis. J Biol Chem 280:41521–41529
McNeill E, Conway SJ, Roderick HL, Bootman MD, Hogg N (2007) Defective chemoattractant-induced calcium signalling in S100A9 null neutrophils. Cell Calcium 41:107–121
Mikkelsen SE, Novitskaya V, Kriajevska M, Berezin V, Bock E, Norrild B, Lukanidin E (2001) S100A12 protein is a strong inducer of neurite outgrowth from primary hippocampal neurons. J Neurochem 79:767–776
Miranda LP, Tao T, Jones A, Chernushevich I, Standing KG, Geczy CL, Alewood PF (2001) Total chemical synthesis and chemotactic activity of human S100A12 (EN-RAGE). FEBS Lett 488:85–90
Mirmohammadsadegh A, Tschakarjan E, Ljoljic A, Bohner K, Michel G, Ruzicka T, Goos M, Hengge UR (2000) Calgranulin C is overexpressed in lesional psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 114:1207–1208
Mogensen TH (2009). Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin Microbiol Rev 22:240–273 (table of contents)
Mork G, Schjerven H, Mangschau L, Soyland E, Brandtzaeg P (2003) Proinflammatory cytokines upregulate expression of calprotectin (L1 protein, MRP-8/MRP-14) in cultured human keratinocytes. Br J Dermatol 149:484–491
Moroz OV, Burkitt W, Wittkowski H, He W, Ianoul A, Novitskaya V, Xie J, Polyakova O, Lednev IK, Shekhtman A, Derrick PJ, Bjoerk P, Foell D, Bronstein IB (2009) Both Ca2 + and Zn2 + are essential for S100A12 protein -oligomerization and function. BMC Biochem 10:11
Murthy AR, Lehrer RI, Harwig SS, Miyasaki KT (1993) In vitro candidastatic properties of the human neutrophil calprotectin complex. J Immunol 151:6291–6301
Nacken W, Roth J, Sorg C, Kerkhoff C (2003) S100A9/S100A8: myeloid representatives of the S100 protein family as prominent players in innate immunity. Microsc Res Tech 60:569–580
Nacken W, Mooren FC, Manitz MP, Bode G, Sorg C, Kerkhoff C (2005) S100A9 deficiency alters adenosine-5′******-triphosphate induced calcium signalling but does not generally interfere with calcium and zinc homeostasis in murine neutrophils. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:1241–1253
Newton RA, Hogg N (1998) The human S100 protein MRP-14 is a novel activator of the beta 2 integrin Mac-1 on neutrophils. J Immunol 160:1427–1435
Nicholls SJ, Hazen SL (2005) Myeloperoxidase and cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:1102–1111
Nishimura F, Terranova VP, Sawa T, Murayama Y (1999) Migration inhibitory factor related protein-8 (MRP-8) is an autocrine chemotactic factor for periodontal ligament cells. J Dent Res 78:1251–1255
Odink K, Cerletti N, Bruggen J, Clerc RG, Tarcsay L, Zwadlo G, Gerhards G, Schlegel R, Sorg C (1987) Two calcium-binding proteins in infiltrate macrophages of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 330:80–82
Orlova VV, Choi EY, Xie C, Chavakis E, Bierhaus A, Ihanus E, Ballantyne CM, Gahmberg CG, Bianchi ME, Nawroth PP, Chavakis T (2007) A novel pathway of HMGB1-mediated inflammatory cell recruitment that requires Mac-1-integrin. EMBO J 26:1129–1139
Otsuka K, Terasaki F, Ikemoto M, Fujita S, Tsukada B, Katashima T, Kanzaki Y, Sohmiya K, Kono T, Toko H, Fujita M, Kitaura Y (2009) Suppression of inflammation in rat autoimmune myocarditis by S100A8/A9 through modulation of the proinflammatory cytokine network. Eur J Heart Fail 11:229–237
Paccola CC, Gutierrez VP, Longo I, Juliano L, Juliano MA, Giorgi R (2008) Antinociceptive effect of the C-terminus of murine S100A9 protein on experimental neuropathic pain. Peptides 29:1806–1814
Pagano RL, Dias MA, Dale CS, Giorgi R (2002) Neutrophils and the calcium-binding protein MRP-14 mediate carrageenan-induced antinociception in mice. Mediators Inflamm 11:203–210
Pagano RL, Sampaio SC, Juliano L, Juliano MA, Giorgi R (2005) The C-terminus of murine S100A9 inhibits spreading and phagocytic activity of adherent peritoneal cells. Inflamm Res 54:204–210
Pagano RL, Mariano M, Giorgi R (2006) Neutrophilic cell-free exudate induces antinociception mediated by the protein S100A9. Mediators Inflamm 2006:36765
Pascual G, Glass CK (2006) Nuclear receptors versus inflammation: mechanisms of transrepression. Trends Endocrinol Metab 17:321–327
Passey RJ, Williams E, Lichanska AM, Wells C, Hu S, Geczy CL, Little MH, Hume DA (1999) A null mutation in the inflammation-associated S100 protein S100A8 causes early resorption of the mouse embryo. J Immunol 163:2209–2216
Perez-Mato I, Castro C, Ruiz FA, Corrales FJ, Mato JM (1999) Methionine adenosyltransferase S-nitrosylation is regulated by the basic and acidic amino acids surrounding the target thiol. J Biol Chem 274:17075–17079
Petri B, Bixel MG (2006) Molecular events during leukocyte diapedesis. FEBS J 273:4399–4407
Petri B, Phillipson M, Kubes P (2008) The physiology of leukocyte recruitment: an in vivo perspective. J Immunol 180:6439–6446
Petty HR, Kindzelskii AL, Adachi Y, Todd RF 3rd (1997) Ectodomain interactions of leukocyte integrins and pro-inflammatory GPI-linked membrane proteins. J Pharm Biomed Anal 15:1405–1416
Petty HR, Worth RG, Todd RF 3rd (2002) Interactions of integrins with their partner proteins in leukocyte membranes. Immunol Res 25:75–95
Propper C, Huang X, Roth J, Sorg C, Nacken W (1999) Analysis of the MRP8-MRP14 protein–protein interaction by the two-hybrid system suggests a prominent role of the C-terminal domain of S100 proteins in dimer formation. J Biol Chem 274:183–188
Raftery MJ, Geczy CL (2002) Electrospray low energy CID and MALDI PSD fragmentations of protonated sulfinamide cross-linked peptides. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 13:709–718
Raftery MJ, Yang Z, Valenzuela SM, Geczy CL (2001) Novel intra- and inter-molecular sulfinamide bonds in S100A8 produced by hypochlorite oxidation. J Biol Chem 276:33393–33401
Rahimi F, Hsu K, Endoh Y, Geczy CL (2005) FGF-2, IL-1beta and TGF-beta regulate fibroblast expression of S100A8. Febs J 272:2811–2827
Rammes A, Roth J, Goebeler M, Klempt M, Hartmann M, Sorg C (1997) Myeloid-related protein (MRP) 8 and MRP14, calcium-binding proteins of the S100 family, are secreted by activated monocytes via a novel, tubulin-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 272:9496–9502
Raptis SZ, Pham CT (2005) Neutrophil-derived serine proteases in immune complex-mediated diseases. Immunol Res 32:211–215
Ravasi T, Hsu K, Goyette J, Schroder K, Yang Z, Rahimi F, Miranda LP, Alewood PF, Hume DA, Geczy C (2004) Probing the S100 protein family through genomic and functional analysis. Genomics 84:10–22
Reed RC, Berwin B, Baker JP, Nicchitta CV (2003) GRP94/gp96 elicits ERK activation in murine macrophages. A role for endotoxin contamination in NF-kappa B activation and nitric oxide production. J Biol Chem 278:31853–31860
Robinson MJ, Hogg N (2000) A comparison of human S100A12 with MRP-14 (S100A9). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 275:865–870
Robinson MJ, Tessier P, Poulsom R, Hogg N (2002) The S100 family heterodimer, MRP-8/14, binds with high affinity to heparin and heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans on endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 277:3658–3665
Roth J, Vogl T, Sorg C, Sunderkotter C (2003) Phagocyte-specific S100 proteins: a novel group of proinflammatory molecules. Trends Immunol 24:155–158
Rouleau P, Vandal K, Ryckman C, Poubelle PE, Boivin A, Talbot M, Tessier PA (2003) The calcium-binding protein S100A12 induces neutrophil adhesion, migration, and release from bone marrow in mouse at concentrations similar to those found in human inflammatory arthritis. Clin Immunol 107:46–54
Ryckman C, McColl SR, Vandal K, de Medicis R, Lussier A, Poubelle PE, Tessier PA (2003a) Role of S100A8 and S100A9 in neutrophil recruitment in response to monosodium urate monohydrate crystals in the air-pouch model of acute gouty arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:2310–2320
Ryckman C, Vandal K, Rouleau P, Talbot M, Tessier PA (2003b) Proinflammatory activities of S100: proteins S100A8, S100A9, and S100A8/A9 induce neutrophil chemotaxis and adhesion. J Immunol 170:3233–3242
Ryckman C, Gilbert C, de Medicis R, Lussier A, Vandal K, Tessier PA (2004) Monosodium urate monohydrate crystals induce the release of the proinflammatory protein S100A8/A9 from neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol 76:433–440
Sakaguchi T, Yan SF, Yan SD, Belov D, Rong LL, Sousa M, Andrassy M, Marso SP, Duda S, Arnold B, Liliensiek B, Nawroth PP, Stern DM, Schmidt AM, Naka Y (2003) Central role of RAGE-dependent neointimal expansion in arterial restenosis. J Clin Invest 111:959–972
Salama I, Malone PS, Mihaimeed F, Jones JL (2008) A review of the S100 proteins in cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 34:357–364
Santhanagopalan V, Hahn BL, Sohnle PG (1995) Resistance of zinc-supplemented Candida albicans cells to the growth inhibitory effect of calprotectin. J Infect Dis 171:1289–1294
Schafer BW, Heizmann CW (1996) The S100 family of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins: functions and pathology. Trends Biochem Sci 21:134–140
Schmidt AM, Yan SD, Yan SF, Stern DM (2001) The multiligand receptor RAGE as a progression factor amplifying immune and inflammatory responses. J Clin Invest 108:949–955
Schnekenburger J, Schick V, Kruger B, Manitz MP, Sorg C, Nacken W, Kerkhoff C, Kahlert A, Mayerle J, Domschke W, Lerch MM (2008) The calcium binding protein S100A9 is essential for pancreatic leukocyte infiltration and induces disruption of cell–cell contacts. J Cell Physiol 216:558–567
Seemann J, Weber K, Gerke V (1996) Structural requirements for annexin I-S100C complex-formation. Biochem J 319(Pt 1):123–129
Sellmayer A, Krane SM, Ouellette AJ, Bonventre JV (1992) 1 alpha, 25-(OH)2 vitamin D3 enhances expression of the genes encoding Ca(2 +)-binding proteins MRP-8 and MRP-14. Am J Physiol 262:C235–C242
Shepherd CE, Goyette J, Utter V, Rahimi F, Yang Z, Geczy CL, Halliday GM (2006) Inflammatory S100A9 and S100A12 proteins in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 27:1554–1563
Shibata F, Miyama K, Shinoda F, Mizumoto J, Takano K, Nakagawa H (2004) Fibroblast growth-stimulating activity of S100A9 (MRP-14). Eur J Biochem 271:2137–2143
Shibata F, Ito A, Ohkuma Y, Mitsui K (2005) Mitogenic activity of S100A9 (MRP-14). Biol Pharm Bull 28:2312–2314
Smith SP, Shaw GS (1998) A change-in-hand mechanism for S100 signalling. Biochem Cell Biol 76:324–333
Sohnle PG, Hunter MJ, Hahn B, Chazin WJ (2000) Zinc-reversible antimicrobial activity of recombinant calprotectin (migration inhibitory factor-related proteins 8 and 14). J Infect Dis 182:1272–1275
Sorci G, Riuzzi F, Agneletti AL, Marchetti C, Donato R (2003) S100B inhibits myogenic differentiation and myotube formation in a RAGE-independent manner. Mol Cell Biol 23:4870–4881
Sorci G, Riuzzi F, Agneletti AL, Marchetti C, Donato R (2004) S100B causes apoptosis in a myoblast cell line in a RAGE-independent manner. J Cell Physiol 199:274–283
Sperandio M (2006) Selectins and glycosyltransferases in leukocyte rolling in vivo. FEBS J 273:4377–4389
Srikrishna G, Panneerselvam K, Westphal V, Abraham V, Varki A, Freeze HH (2001) Two proteins modulating transendothelial migration of leukocytes recognize novel carboxylated glycans on endothelial cells. J Immunol 166:4678–4688
Sroussi HY, Berline J, Dazin P, Green P, Palefsky JM (2006) S100A8 triggers oxidation-sensitive repulsion of neutrophils. J Dent Res 85:829–833
Sroussi HY, Berline J, Palefsky JM (2007) Oxidation of methionine 63 and 83 regulates the effect of S100A9 on the migration of neutrophils in vitro. J Leukoc Biol 81:818–824
Sroussi HY, Kohler GA, Agabian N, Villines D, Palefsky JM (2009) Substitution of methionine 63 or 83 in S100A9 and cysteine 42 in S100A8 abrogate the antifungal activities of S100A8/A9: potential role for oxidative regulation. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 55:55–61
Steinbakk M, Naess-Andresen CF, Lingaas E, Dale I, Brandtzaeg P, Fagerhol MK (1990) Antimicrobial actions of calcium binding leucocyte L1 protein, calprotectin. Lancet 336:763–765
Sunahori K, Yamamura M, Yamana J, Takasugi K, Kawashima M, Yamamoto H, Chazin WJ, Nakatani Y, Yui S, Makino H (2006) The S100A8/A9 heterodimer amplifies proinflammatory cytokine production by macrophages via activation of nuclear factor kappa B and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R69
Suryono Kido J, Hayashi N, Kataoka M, Shinohara Y, Nagata T (2006) Norepinephrine stimulates calprotectin expression in human monocytic cells. J Periodontal Res 41:159–164
Terasaki F, Fujita M, Shimomura H, Tsukada B, Otsuka K, Katashima T, Ikemoto M, Kitaura Y (2007) Enhanced expression of myeloid-related protein complex (MRP8/14) in macrophages and multinucleated giant cells in granulomas of patients with active cardiac sarcoidosis. Circ J 71:1545–1550
Test S, Weiss SJ (1986) The generation and utilization of chlorinated oxidants by human neutrophils. Adv Free Radic Biol Med 2:91–116
Thorey IS, Roth J, Regenbogen J, Halle JP, Bittner M, Vogl T, Kaesler S, Bugnon P, Reitmaier B, Durka S, Graf A, Wockner M, Rieger N, Konstantinow A, Wolf E, Goppelt A, Werner S (2001) The Ca2 + -binding proteins S100A8 and S100A9 are encoded by novel injury-regulated genes. J Biol Chem 276:35818–35825
Tian J, Avalos AM, Mao SY, Chen B, Senthil K, Wu H, Parroche P, Drabic S, Golenbock D, Sirois C, Hua J, An LL, Audoly L, La Rosa G, Bierhaus A, Naworth P, Marshak-Rothstein A, Crow MK, Fitzgerald KA, Latz E, Kiener PA, Coyle AJ (2007) Toll-like receptor 9-dependent activation by DNA-containing immune complexes is mediated by HMGB1 and RAGE. Nat Immunol 8:487–496
Todd RF 3rd, Petty HR (1997) Beta 2 (CD11/CD18) integrins can serve as signaling partners for other leukocyte receptors. J Lab Clin Med 129:492–498
Tsan MF, Gao B (2004) Endogenous ligands of Toll-like receptors. J Leukoc Biol 76:514–519
Turovskaya O, Foell D, Sinha P, Vogl T, Newlin R, Nayak J, Nguyen M, Olsson A, Nawroth PP, Bierhaus A, Varki N, Kronenberg M, Freeze HH, Srikrishna G (2008) RAGE, carboxylated glycans and S100A8/A9 play essential roles in colitis-associated carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 29:2035–2043
van Lent PL, Grevers L, Blom AB, Sloetjes A, Mort JS, Vogl T, Nacken W, van den Berg WB and Roth J (2007) Myeloid related proteins S100A8/S100A9 regulate joint inflammation and cartilage destruction during antigen-induced arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis
Vandal K, Rouleau P, Boivin A, Ryckman C, Talbot M, Tessier PA (2003) Blockade of S100A8 and S100A9 suppresses neutrophil migration in response to lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol 171:2602–2609
Viemann D, Strey A, Janning A, Jurk K, Klimmek K, Vogl T, Hirono K, Ichida F, Foell D, Kehrel B, Gerke V, Sorg C, Roth J (2005) Myeloid-related proteins 8 and 14 induce a specific inflammatory response in human microvascular endothelial cells. Blood 105:2955–2962
Viemann D, Barczyk K, Vogl T, Fischer U, Sunderkotter C, Schulze-Osthoff K, Roth J (2007) MRP8/MRP14 impairs endothelial integrity and induces a caspase-dependent and -independent cell death program. Blood 109:2453–2460
Voganatsi A, Panyutich A, Miyasaki KT, Murthy RK (2001) Mechanism of extracellular release of human neutrophil calprotectin complex. J Leukoc Biol 70:130–134
Vogl T, Propper C, Hartmann M, Strey A, Strupat K, van den Bos C, Sorg C, Roth J (1999a) S100A12 is expressed exclusively by granulocytes and acts independently from MRP8 and MRP14. J Biol Chem 274:25291–25296
Vogl T, Roth J, Sorg C, Hillenkamp F, Strupat K (1999b) Calcium-induced noncovalently linked tetramers of MRP8 and MRP14 detected by ultraviolet matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 10:1124–1130
Vogl T, Ludwig S, Goebeler M, Strey A, Thorey IS, Reichelt R, Foell D, Gerke V, Manitz MP, Nacken W, Werner S, Sorg C, Roth J (2004) MRP8 and MRP14 control microtubule reorganization during transendothelial migration of phagocytes. Blood 104:4260–4268
Vogl T, Leukert N, Barczyk K, Strupat K, Roth J (2006) Biophysical characterization of S100A8 and S100A9 in the absence and presence of bivalent cations. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763:1298–1306
Vogl T, Tenbrock K, Ludwig S, Leukert N, Ehrhardt C, van Zoelen MA, Nacken W, Foell D, van der Poll T, Sorg C, Roth J (2007) Mrp8 and Mrp14 are endogenous activators of Toll-like receptor 4, promoting lethal, endotoxin-induced shock. Nat Med 13:1042–1049
Wilckens T (1995) Glucocorticoids and immune function: physiological relevance and pathogenic potential of hormonal dysfunction. Trends Pharmacol Sci 16:193–197
Wolf R, Howard OM, Dong HF, Voscopoulos C, Boeshans K, Winston J, Divi R, Gunsior M, Goldsmith P, Ahvazi B, Chavakis T, Oppenheim JJ, Yuspa SH (2008) Chemotactic activity of S100A7 (Psoriasin) is mediated by the receptor for advanced glycation end products and potentiates inflammation with highly homologous but functionally distinct S100A15. J Immunol 181:1499–1506
Wu N, Davidson JM (2004) Migration inhibitory factor-related protein (MRP)8 and MRP14 are differentially expressed in free-electron laser and scalpel incisions. Wound Repair Regen 12:327–336
Xie J, Burz DS, He W, Bronstein IB, Lednev I, Shekhtman A (2007) Hexameric calgranulin C (S100A12) binds to the receptor for advanced glycated end products (RAGE) using symmetric hydrophobic target-binding patches. J Biol Chem 282:4218–4231
Xu K, Geczy CL (2000) IFN-gamma and TNF regulate macrophage expression of the chemotactic S100 protein S100A8. J Immunol 164:4916–4923
Xu K, Yen T, Geczy CL (2001) Il-10 up-regulates macrophage expression of the S100 protein S100A8. J Immunol 166:6358–6366
Yan WX, Armishaw C, Goyette J, Yang Z, Cai H, Alewood P, Geczy CL (2008) Mast cell and monocyte recruitment by S100A12 and its hinge domain. J Biol Chem 283:13035–13043
Yanamandra K, Alexeyev O, Zamotin V, Srivastava V, Shchukarev A, Brorsson AC, Tartaglia GG, Vogl T, Kayed R, Wingsle G, Olsson J, Dobson CM, Bergh A, Elgh F, Morozova-Roche LA (2009) Amyloid formation by the pro-inflammatory S100A8/A9 proteins in the ageing prostate. PLoS ONE 4:e5562
Yang Z, Tao T, Raftery MJ, Youssef P, Di Girolamo N, Geczy CL (2001) Proinflammatory properties of the human S100 protein S100A12. J Leukoc Biol 69:986–994
Yang Z, Yan WX, Cai H, Tedla N, Armishaw C, Di Girolamo N, Wang HW, Hampartzoumian T, Simpson JL, Gibson PG, Hunt J, Hart P, Hughes JM, Perry MA, Alewood PF, Geczy CL (2007) S100A12 provokes mast cell activation: a potential amplification pathway in asthma and innate immunity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 119:106–114
Yen T, Harrison CA, Devery JM, Leong S, Iismaa SE, Yoshimura T, Geczy CL (1997) Induction of the S100 chemotactic protein, CP-10, in murine microvascular endothelial cells by proinflammatory stimuli. Blood 90:4812–4821
Yong HY, Moon A (2007) Roles of calcium-binding proteins, S100A8 and S100A9, in invasive phenotype of human gastric cancer cells. Arch Pharm Res 30:75–81
Yui S, Mikami M, Yamazaki M (1995) Purification and characterization of the cytotoxic factor in rat peritoneal exudate cells: its identification as the calcium binding protein complex, calprotectin. J Leukoc Biol 58:307–316
Yui S, Mikami M, Tsurumaki K, Yamazaki M (1997) Growth-inhibitory and apoptosis-inducing activities of calprotectin derived from inflammatory exudate cells on normal fibroblasts: regulation by metal ions. J Leukoc Biol 61:50–57
Yui S, Nakatani Y, Hunter MJ, Chazin WJ, Yamazaki M (2002) Implication of extracellular zinc exclusion by recombinant human calprotectin (MRP8 and MRP14) from target cells in its apoptosis-inducing activity. Mediators Inflamm 11:165–172
Zimmer DB, Wright Sadosky P, Weber DJ (2003) Molecular mechanisms of S100–target protein interactions. Microsc Res Tech 60:552–559
Zreiqat H, Howlett CR, Gronthos S, Hume D, Geczy CL (2007) S100A8/S100A9 and their association with cartilage and bone. J Mol Histol 38:381–391
Zwadlo G, Bruggen J, Gerhards G, Schlegel R, Sorg C (1988) Two calcium-binding proteins associated with specific stages of myeloid cell differentiation are expressed by subsets of macrophages in inflammatory tissues. Clin Exp Immunol 72:510–515
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia for funding and members of the laboratory who contributed to the research discussed in this review, particularly Dr. Kenneth Hsu, Ms. Su Yin Lim, Dr. Zheng Yang, Dr. Weixing Yan and Dr. Mark Raftery and our long-term collaborator, Professor Paul Alewood.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyette, J., Geczy, C.L. Inflammation-associated S100 proteins: new mechanisms that regulate function. Amino Acids 41, 821–842 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0528-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0528-0