Abstract
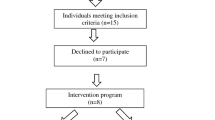
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) technique is a dual-channel electrotherapy system designed specifically for the treatment of pharyngeal dysfunction. The purpose of this study was to evaluate and compare the outcome of NMES versus traditional swallowing therapy (TT) in stroke patients. Three European swallowing centers participated in this randomized trial. Twenty-five patients (16 men and 9 women) were included. Twelve patients were randomized for NMES and 13 for TT. Mean age was 70 years for the NMES group and 71 years for the TT group. Inclusion criteria were (1) patients 50–80 years old with cerebrovascular disease (stroke) for more than 3 months before the study, (2) only patients with hemispheric stroke, (3) no brainstem involvement, (4) ability to swallow, and (5) ability to communicate. Pre- and post-trial measurements were videoradiographic swallowing evaluation, nutritional status, oral motor function test, and a visual analog scale (VAS) for self-evaluation of complaints. All subjects received 15 therapy sessions. Statistically significant positive therapy effects for both NMES and TT combined were found, but there was no statistically significant difference in therapy effect between the groups. The correlations between measurements were low. The patient’s subjective experience of improvement had low correlation with the outcome from the objective evaluation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin RE, Sessle BJ. The role of the cerebral cortex in swallowing. Dysphagia 1993;8:195–202.
Miller AJ. Deglutition. Physiol Rev 1982;62:129–184.
Park CL, O’Neill PA, Martin DF. A pilot exploratory study of oral electrical stimulation on swallow function following stroke: an innovative technique. Dysphagia 1997;12:161–166.
Leelamanit V, Limsakul C, Geater A. Synchronized electrical stimulation in treating pharyngeal dysphagia. Laryngoscope 2002;112:2204–2210.
Hamdy S, Jilani S, Price V, Parker C, Hall N, Power M. Modulation of human swallowing behaviour by thermal and chemical stimulation in health and after brain injury. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2003;15:69–77.
Hamdy S, Rothwell JC, Aziz Q, Thompson DG. Organization and reorganization of human swallowing motor cortex: implications for recovery after stroke. Clin Sci 2000;99:151–157.
Fraser C, Power M, Hamdy S, Rothwell J, Hobday D, Hollander I, Tyrell P, Hobson A, Williams S, Thompson D. Driving plasticity in human adult motor cortex is associated with improved motor function after brain injury. Neuron 2002;34:831–840.
Hamdy S, Rothwell JC, Fraser C, Power M, Gow D, Thompson DG. Patterns of excitability in human oesophageal sensorimotor cortex to painful and nonpainful visceral stimulation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2002;282:G332–G337.
Fraser C, Rothwell J, Power M, Hobson A, Thompson D, Hamdy S. Differential changes in human pharyngoesophageal motor excitability induced by swallowing, pharyngeal stimulation, and anaesthesia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2003;285:G137–G144.
Ertekin C, Turman B, Tarlaci S, Celik M, Aydogdu I, Secil Y, Kiylioglu N. Cricopharyngeal sphincter muscle responses to transcranial magnetic stimulation in normal subjects and in patients with dysphagia. Clin Neurophysiol 2001;112:86–94.
Mattioli S, Lugaresi M, Zannoli R, Brusori S, d’Ovidio F, Braccaioli L. Pharyngoesophageal manometry with an original balloon sensor probe for the study of oropharyngeal dysphagia. Dysphagia 2003;18:242–248.
Freed M, Wijting Y. VitalStim Certification Program. Training manual for patient assessment, treatment using VitalStim electrical stimulation. Hixson TN: Chattanooga Group; 2003.
Suiter DM, Leder SB, Ruark JL. Effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation on submental muscle activity. Dysphagia 2006;21:56–60.
Kiger M, Brown CS, Watkins L. Dysphagia management: An analysis of patient outcomes using VitalStim™ therapy compared to traditional swallow therapy. Dysphagia 2006;21:243–253.
Ludlow CL, Humbert I, Saxon K, Poletto C, Sonies B, Crujido L. Effects of surface electrical stimulation both at rest and during swallowing in chronic pharyngeal dysphagia. Dysphagia 2007;22:1–10.
Shaw GY, Sechtem PR, Searl J, Keller K, Rawi TA, Dowdy E. Transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation (VitalStim) curative therapy for severe dysphagia: myth or reality? Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2007;116:36–44.
Logemann JA. The effects of VitalStim on clinical and research thinking in dysphagia. Dysphagia 2007;22:11–12.
Bülow M. Therapeutic aspects of oral and pharyngeal swallowing dysfunction. Videoradiographic and videomanometric analyses of adult healthy volunteers and dysphagic patients. Thesis, Faculty of Medicine, Lund University, 2003.
Gerek M, Ciyiltepe M. The management of swallowing disorders through rehabilitation methods. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ithis Derg 2005;14:10–17.
Zammit-Maempel I, Chapple C-L, Leslie P. Radiation dose in videofluoroscopic swallow studies. Dysphagia 2007;22:13–15.
Elmståhl S, Bülow M, Ekberg O, Pettersson M, Tegner H. Treatment of dysphagia improves nutritional conditions in stroke patients. Dysphagia 1999;14:61–66.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Corina van As and Stella Ramette, Atos Medical Sweden, for their assistance in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bülow, M., Speyer, R., Baijens, L. et al. Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES) in Stroke Patients with Oral and Pharyngeal Dysfunction. Dysphagia 23, 302–309 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9145-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9145-9