Abstract
Background
We evaluated serum (s) cystatin C (CysC) and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and urine (u) CysC, NGAL and kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) as markers of acute kidney injury (AKI) in asphyxiated neonates.
Methods
AKI biomarkers were measured in 13 asphyxiated neonates born at ≥36 weeks gestational age (eight with AKI and five without AKI) and 22 controls. AKI was defined as serum creatinine ≥1.5 mg/dl for >24 h or rising values >0.3 mg/dl from day of life (DOL) 1. Biomarkers were measured on DOL 1, 3, and 10.
Results
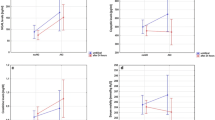
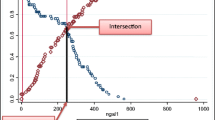
Asphyxiated neonates had significantly higher sCysC on DOL 1 as well as sNGAL and uCysC and uNGAL (standardized to urine creatinine and absolute values) than controls at all time points. Compared to controls, significantly higher sNGAL, uCysC, and uNGAL values were observed in the asphyxia-AKI and asphyxia–no AKI subgroups. Regarding uKIM-1, only the absolute values were significantly higher in asphyxiated neonates (DOL 10). sNGAL, uCyst, and uNGAL had a significant diagnostic performance as predictors AKI on DOL 1.
Conclusions
sNGAL, uCysC, and uNGAL are sensitive, early AKI biomarkers, increasing significantly in asphyxiated neonates even in those not fulfilling AKI criteria. Their measurement on DOL 1 is predictive of post-asphyxia-AKI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shah P, Riphagen S, Beyene J, Perlman M (2004) Multiorgan dysfunction in infants with post-asphyxial hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 89:F152–155
Gupta BD, Sharma P, Bagla J, Parakh M, Soni JP (2005) Renal failure in asphyxiated neonates. Indian Pediatr 42:928–934
Perlman JM, Tack ED (1988) Renal injury in the asphyxiated newborn infant: relationship to neurologic outcome. J Pediatr 113:875–879
Askenazi DJ, Ambalavanan N, Goldstein SL (2009) Acute kidney injury in critically ill newborns: what do we know? What do we need to learn? Pediatr Nephrol 24:265–274
Jenik AG, Ceriani Cernadas JM, Gorenstein A, Ramirez JA, Vain N, Armadans M, Ferraris JR (2000) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the effects of prophylactic theophylline on renal function in term neonates with perinatal asphyxia. Pediatrics 105:E45
Bagshaw SM, Bellomo R (2010) Cystatin C in acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Crit Care. doi:10.1097/MCC.0b013e32833e8412
Ahlström A, Tallgren M, Peltonen S, Pettilä V (2004) Evolution and predictive power of serum cystatin C in acute renal failure. Clin Nephrol 62:344–350
Herget-Rosenthal S, Marggraf G, Hüsing J, Göring F, Pietruck F, Janssen O, Philipp T, Kribben A (2004) Early detection of acute renal failure by serum cystatin C. Kidney Int 66:1115–1122
Herrero-Morín JD, Málaga S, Fernández N, Rey C, Diéguez MA, Solís G, Concha A, Medina A (2007) Cystatin C and beta2-microglobulin: markers of glomerular filtration in critically ill children. Crit Care 11:R59
Nejat M, Pickering JW, Walker RJ, Endre ZH (2010) Rapid detection of acute kidney injury by plasma cystatin C in the intensive care unit. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:3283–3289
Herget-Rosenthal S, van Wijk JA, Bröcker-Preuss M, Bökenkamp A (2007) Increased urinary cystatin C reflects structural and functional renal tubular impairment independent of glomerular filtration rate. Clin Biochem 40:946–951
Nejat M, Pickering JW, Walker RJ, Westhuyzen J, Shaw GM, Frampton CM, Endre ZH (2010) Urinary cystatin C is diagnostic of acute kidney injury and sepsis, and predicts mortality in the intensive care unit. Crit Care 14:R85
Koyner JL, Bennett MR, Worcester EM, Ma Q, Raman J, Jeevanandam V, Kasza KE, O'Connor MF, Konczal DJ, Trevino S, Devarajan P, Murray PT (2008) Urinary cystatin C as an early biomarker of acute kidney injury following adult cardiothoracic surgery. Kidney Int 74:1059–1069
Malyszko J, Bachorzewska-Gajewska H, Poniatowski B, Malyszko JS, Dobrzycki S (2009) Urinary and serum biomarkers after cardiac catheterization in diabetic patients with stable angina and without severe chronic kidney disease. Ren Fail 31:910–919
Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M, Zahedi K, Yang J, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2003) Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2534–2543
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, Ruff SM, Zahedi K, Shao M, Bean J, Mori K, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2005) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet 365:1231–1238
Wagener G, Jan M, Kim M, Mori K, Barasch JM, Sladen RN, Lee HT (2006) Association between increases in urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and acute renal dysfunction after adult cardiac surgery. Anesthesiology 105:485–491
Haase-Fielitz A, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Story D, Matalanis G, Dragun D, Haase M (2009) Novel and conventional serum biomarkers predicting acute kidney injury in adult cardiac surgery–a prospective cohort study. Crit Care Med 37:553–560
Parikh CR, Devarajan P, Zappitelli M, Sint K, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Li S, Kim RW, Koyner JL, Coca SG, Edelstein CL, Shlipak MG, Garg AX, Krawczeski CD, TRIBE-AKI Consortium (2011) Postoperative biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and poor outcomes after pediatric cardiac surgery. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1737–1747
Hall IE, Yarlagadda SG, Coca SG, Wang Z, Doshi M, Devarajan P, Han WK, Marcus RJ, Parikh CR (2010) IL-18 and urinary NGAL predict dialysis and graft recovery after kidney transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:189–197
Bagshaw SM, Bennett M, Haase M, Haase-Fielitz A, Egi M, Morimatsu H, D'amico G, Goldsmith D, Devarajan P, Bellomo R (2010) Plasma and urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in septic versus non-septic acute kidney injury in critical illness. Intensive Care Med 36:452–461
Ichimura T, Hung CC, Yang SA, Stevens JL, Bonventre JV (2004) Kidney injury molecule-1: a tissue and urinary biomarker for nephrotoxicant-induced renal injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F552–563
Han WK, Waikar SS, Johnson A, Betensky RA, Dent CL, Devarajan P, Bonventre JV (2008) Urinary biomarkers in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 73:863–869
Koyner JL, Vaidya VS, Bennett MR, Ma Q, Worcester E, Akhter SA, Raman J, Jeevanandam V, O'Connor MF, Devarajan P, Bonventre JV, Murray PT (2010) Urinary biomarkers in the clinical prognosis and early detection of acute kidney injury. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:2154–2165
Finney H, Newman DJ, Thakkar H, Fell JM, Price CP (2000) Reference ranges for plasma cystatin C and creatinine measurements in premature infants, neonates, and older children. Arch Dis Child 82:71–75
Askenazi DJ, Koralkar R, Levitan EB, Goldstein SL, Devarajan P, Khandrika S, Mehta RL, Ambalavanan N (2011) Baseline values of candidate urine acute kidney injury biomarkers vary by gestational age in premature infants. Pediatr Res 70:302–306
Lavery AP, Meinzen-Derr JK, Anderson E, Ma Q, Bennett MR, Devarajan P, Schibler KR (2008) Urinary NGAL in premature infants. Pediatr Res 64:423–428
Krawczeski CD, Woo JG, Wang Y, Bennett MR, Ma Q, Devarajan P (2011) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin concentrations predict development of acute kidney injury in neonates and children after cardiopulmonary bypass. J Pediatr 158:1009–1015.e1
Askenazi DJ, Montesanti A, Hunley H, Koralkar R, Pawar P, Shuaib F, Liwo A, Devarajan P, Ambalavanan N (2011) Urine biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and mortality in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr 159:907–12.e1
Sarnat HB, Sarnat MS (1976) Neonatal encephalopathy following fetal distress: a clinical and electroencephalographic study. Arch Neurol 33:695–706
Chaturvedi S, Farmer T, Kapke GF (2009) Assay validation for KIM-1: human urinary renal dysfunction biomarker. Int J Biol Sci 5:128–134
Cataldi L, Mussap M, Bertelli L, Ruzzante N, Fanos V, Plebani M (1999) Cystatin C in healthy women at term pregnancy and in their infant newborns: relationship between maternal and neonatal serum levels and reference values. Am J Perinatol 16:287–295
O'Connell AE, Boyce AC, Lumbers ER, Gibson KJ (2003) The effects of asphyxia on renal function in fetal sheep at midgestation. J Physiol 552:933–943
Ikeda T, Murata Y, Quilligan EJ, Parer JT, Murayama T, Koono M (2000) Histologic and biochemical study of the brain, heart, kidney, and liver in asphyxia caused by occlusion of the umbilical cord in near-term fetal lambs. Am J Obstet Gynecol 182:449–457
Willis F, Summers J, Minutillo C, Hewitt I (1997) Indices of renal tubular function in perinatal asphyxia. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 77:F57–60
Roberts DS, Haycock GB, Dalton RN, Turner C, Tomlinson P, Stimmler L, Scopes JW (1990) Prediction of acute renal failure after birth asphyxia. Arch Dis Child 65:1021–1028
Zappitelli M, Washburn KK, Arikan AA, Loftis L, Ma Q, Devarajan P, Parikh CR, Goldstein SL (2007) Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is an early marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care 11:R84
Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Schlattmann P, Haase-Fielitz A, NGAL Meta-analysis Investigator Group (2009) Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 54:1012–1024
Jang HR, Rabb H (2009) The innate immune response in ischemic acute kidney injury. Clin Immunol 130:41–50
El-Achkar TM, Hosein M, Dagher PC (2008) Pathways of renal injury in systemic gram-negative sepsis. Eur J Clin Invest 38:39–44
Hoffmann D, Fuchs TC, Henzler T, Matheis KA, Herget T, Dekant W, Hewitt P, Mally A (2010) Evaluation of a urinary kidney biomarker panel in rat models of acute and subchronic nephrotoxicity. Toxicology 277:49–58
Nykjaer A, Schambye H, Pedersen AH, Nielsen H (2009) Assessing low-dose gentamicin-induced kidney injury in rats by analysis of urine. J Pharmacol Toxicol Meth 60:316–320
Waikar SS, Sabbisetti VS, Bonventre JV (2010) Normalization of urinary biomarkers to creatinine during changes in glomerular filtration rate. Kidney Int 78:486–494
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarafidis, K., Tsepkentzi, E., Agakidou, E. et al. Serum and urine acute kidney injury biomarkers in asphyxiated neonates. Pediatr Nephrol 27, 1575–1582 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-012-2162-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-012-2162-4