Summary
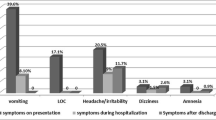
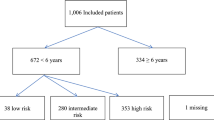
The clincal course of patients admitted following minor head injuries (Glasgow Coma Score [GCS] 13–15) has been studied less extensively than in severely head injured patients. Admission criteria, methods and indications for radiological evaluation are controversial. To study this further, a retrospective review of 633 patients admitted following such injuries to King Khalid University Hospital between 1986 and 1993 was undertaken. Their ages ranged from one month to 80 years (average 17 years). The mechanisms of injury were mainly falls in 339 (53.5%) cases and road traffic accidents in 234 (37%). None of the cases resulted from a non-accidental injury. Radiological evaluation was by skull radiography in 616 (97.3%) cases followed by CT scan in 131 (20.7%). These studies revealed a skull fracture in 78 (12.7%) cases. Six of these 78 patients with skull fracture required a neurosurgical procedure during the first week post injury. These represented 0.97% of the cases who had skull radiographs. A base of skull fracture was an ominous sign, since 3 of the 5 cases with such fractures required ventilation of which one resulted in the only mortality of this series, the fourth developed meningitis. Of the cases studied, 3 (0.5%) developed growing skull fractures all had the initial injury during their first year of life. Other complications were as follows: 25 (3.9%) early post-traumatic seizures, 10 (1.6%) chronic subdural haematomas, 9 (1.4%) extradural haematomas, 2 (0.3%) post-traumatic hydrocephalus and one (0.2%) cerebral abscess. We conclude that patients who have an abnormal GCS, a neurological deficit, post-traumatic seizure, signs or suspicion of basal or depressed skull fracture should be admitted for observation because of the risk of deterioration. Patients with a history of loss of consciousness or amnesia without any of the previous may be discharged to be observed at home by a competent observer, otherwise, will need admission for observation. Radiological evaluation once indicated must be by CT scan. There is no benefit from immediate skull radiography in the initial evaluation of minor head injuries. The indications for CT are an abnormal GCS, presence of neurological deficit, signs of basilar or depressed fracture and persistent or progressive headache or vomiting. Infants with minor injuries should be followed up at least once after two to three months for possible growing fractures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murshid, W. Management of Minor Head Injuries: Admission Criteria, Radiological Evaluation and Treatment of Complications. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 140, 56–64 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007010050058
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007010050058