Abstract
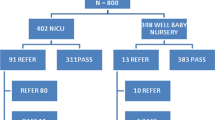
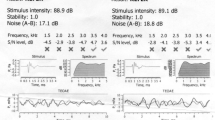
To identify potential risk factors for hearing loss from the infant with high risk criteria as guided by the Joint Committee on Infant Hearing (JCIH, 2000). 490 infants with age range of 2 days to 6 months who had undergone detailed audiological evaluation during for the period of 3 years at Gauhati Medical College Hospital were taken for the study. The hearing screening was performed on each infant using Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emission (DPOAE) testing. The infants who failed DPOAEs screening were followed up and Auditory Brainstem Response testing. Out of 490 high risk infants who had undergone detailed audiological evaluation 145 infants were found to be having hearing loss. Out of 145 infants 73 infants were male and 72 infants were female. The risk factor for hearing loss with the highest incidence was hyperbilirubenemia, Apgar scores of 0–4 at 1 min or 0–6 at 5 min was the second most prevalent risk factor, followed by TORCH infections. This study suggests the need for review of high risk register that is used along with the physiological and electrophysiological hearing test to screen the infants. The high risk register remains helpful in determining follow up plans so that children who may develop late onset of hearing loss will not be missed. Being aware of which risk factors are more likely to cause hearing loss in infants would be helpful to plan for follow up these children.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beata AS, Ioana AN (2008) Etiopathogeny of congenital and early-onset hearing loss; detection and early intervention methods in infants and children. J Clin Med 3(1):45–51
Downs M (2004) The case for detection and intervention at birth. Semin Hearing 15:76–83
Joint committee on infant hearing. Position statement (1994) American Speech, Language and Hearing Association 36(12):38–41
Joint committee on infant hearing (2000) Position statement: Principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Cited from http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/ehdi/documents/jcihyr2000.pdf
Meyer C, Wittle J, Hiildmann A, Hennecke H, Schunck U, Maul K et al (1999) Neonatal screening for hearing disorder in infants at risk: incidence, risk factors, and follow-up. Pediatrics 104(4):900–904
Shimizu H, Walters RJ, Proctor LR, Kennedy DW, Allen MC, Markowitz RK (1990) Identification of hearing impairment in the neonatal intensive care unit population: outcome of a five-year project at the Johns Hopkins hospital. Semin Hearing 11(2):150–160
Swigonski N, Shallop J, Bull MJ, Lemons A (1987) Hearing screening of high risk newborns. Ear Hear 8(1):26–30
Yoshikawa S, Ikeda K, Kudo T, Kobayashi T (2004) The effects of hypoxia, premature birth, infection, ototoxic drugs, circulatory systems and congenital disease on neonatal hearing loss. Auris Nasus Larynx 31:361–368
Yoshinaga-Itano C (2004) Levels of evidence: universal newborn hearing screening (UNHS) and early detection and intervention systems (EHDI). J Commun Disord 37:451–465
Yoshinaga-Itano C, Gravel JS (2001) The evidence for universal newborn hearing screening. Am J Audiol 10:62–64
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biswas, A.K., Goswami, S.C., Baruah, D.K. et al. The Potential Risk Factors and the Identification of Hearing Loss in Infants. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 64, 214–217 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0307-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0307-6